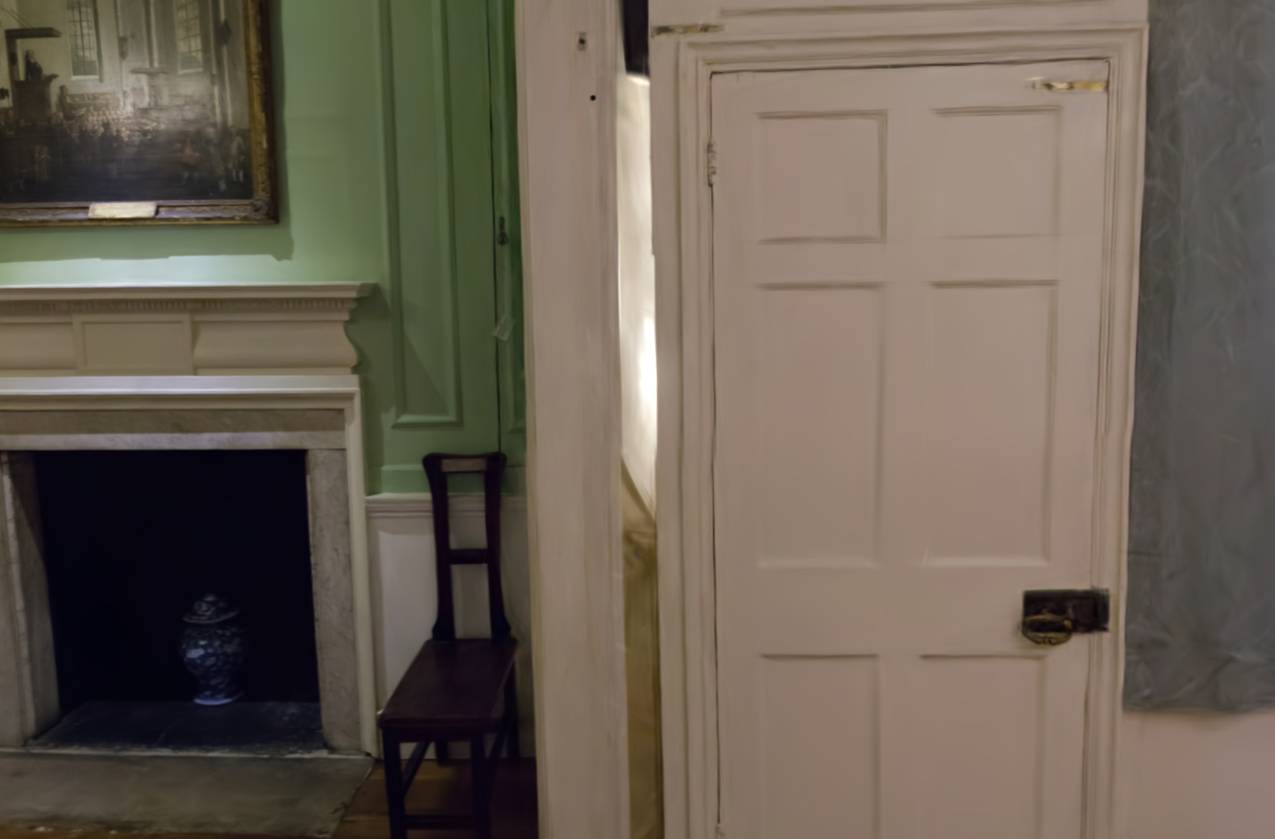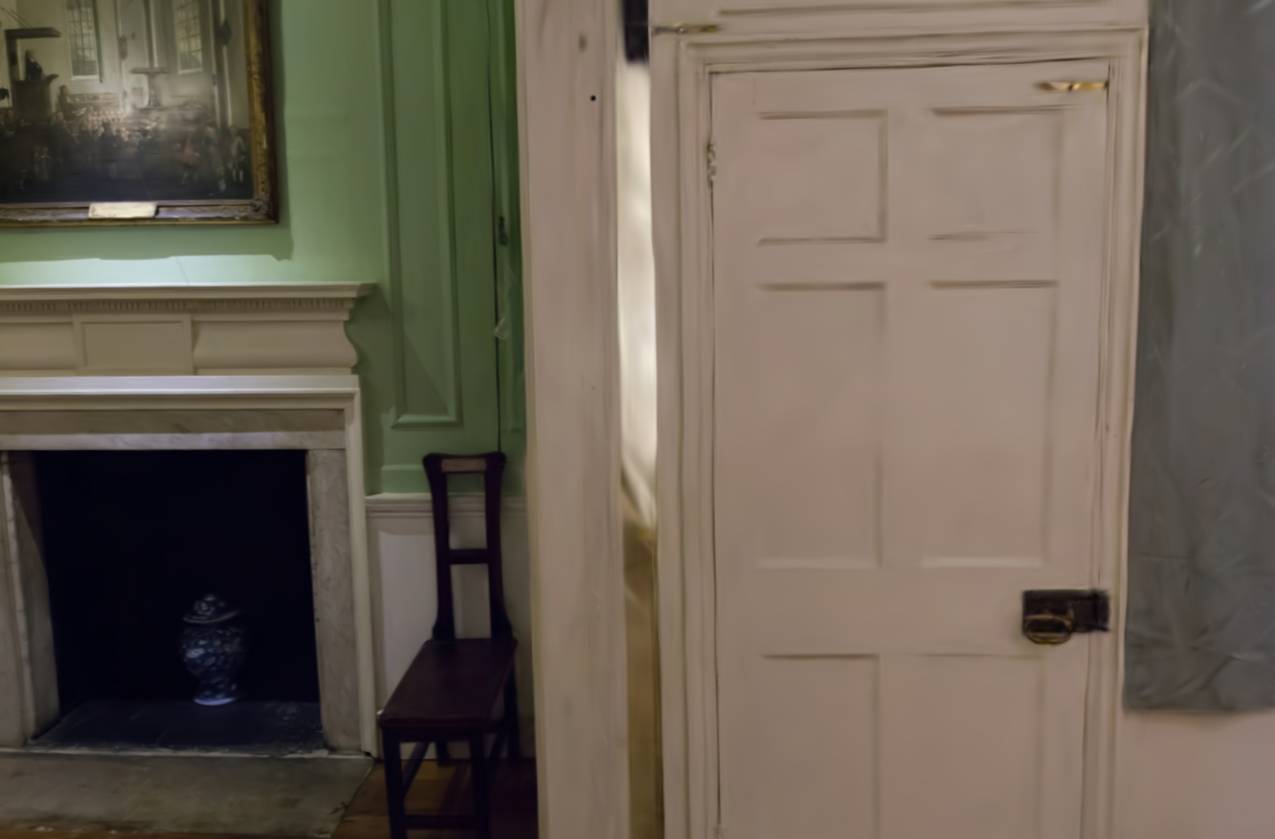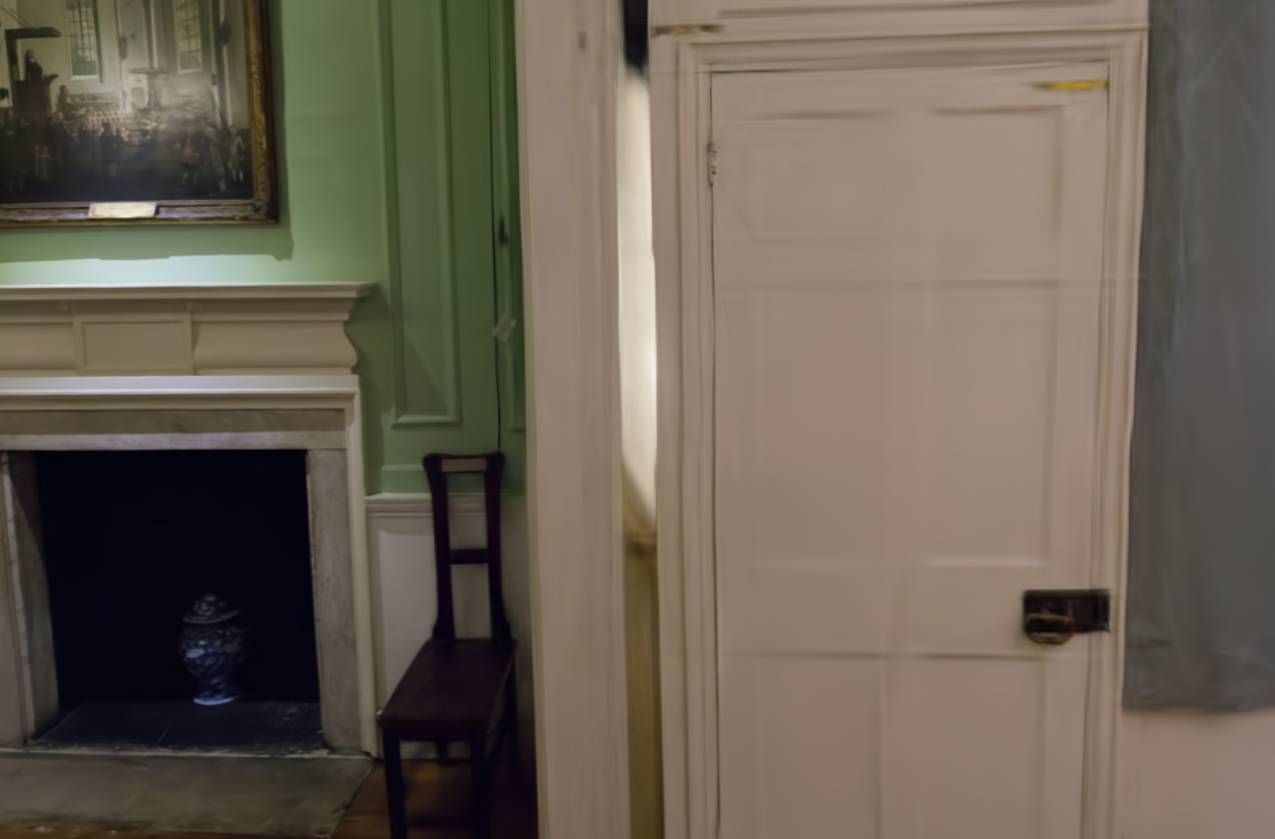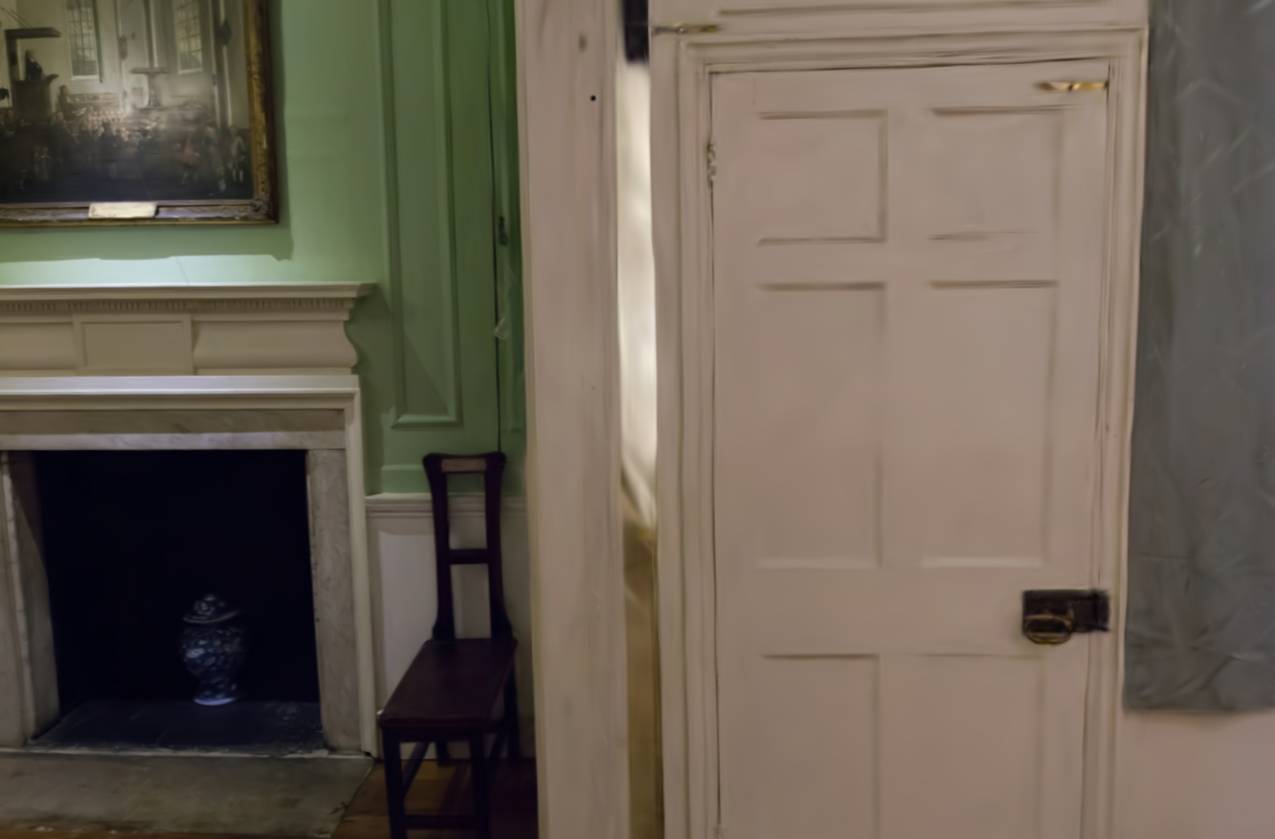Abstract
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has revolutionized novel view synthesis with high-quality rendering through continuous aggregations of millions of 3D Gaussian primitives. However, it suffers from a substantial memory footprint, particularly during training due to uncontrolled densification, posing a critical bottleneck for deployment on memory-constrained edge devices. While existing methods prune redundant Gaussians post-training, they fail to address the peak memory spikes caused by the abrupt growth of Gaussians early in the training process. To solve the training memory consumption problem, we propose a systematic training framework that dynamically grows, identifies, and removes Gaussians in an iterative way, where the growth and removal are alternatively performed in each iteration. In other words, the proposed framework alternates between incremental pruning of low-impact Gaussians and strategic growing of new primitives with an adaptive Gaussian compensation, maintaining a near-constant low memory usage while progressively refining rendering fidelity. We comprehensively evaluate the proposed training framework on various real-world datasets under strict memory constraints, showing significant improvements over existing state-of-the-art methods. Particularly, our proposed method practically enables memory-efficient 3DGS training on NVIDIA Jetson AGX Xavier, achieving similar visual quality with up to 80% lower peak training memory consumption than the original 3DGS.
Method Overview

We propose a memory-bounded 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) training framework that dynamically adapts the number of Gaussians during optimization to ensure both high rendering quality and memory efficiency. Our method alternates between three main stages: Growing, Compensation, and Pruning, iteratively refining the model.
- Growing: A novel clone-and-split strategy increases the number of Gaussians based on position and color gradients, then move cloned Gaussians to appropriate places by accumulated gradient information, rapidly densifying and refining the scene representation.
- Compensation: Underfitting regions are addressed by identifying high-error pixels and generating new Gaussians at their corresponding 3D locations using depth alpha blending.
- Pruning: To maintain a fixed memory budget, the least important Gaussians are removed using importance-based criterion, ensuring efficient training without sacrificing quality.
By continuously alternating between these steps, our framework learns an optimized, compact Gaussian representation that achieves high-fidelity rendering while staying within a limited trianing memory usage.